Infectious diseases
Discover everything there is to know about the speciality of infectious diseases: what microbiology is, what parasitology, virology or mycology involve and how a microbiological diagnosis is carried out. We tell you which are the main infectious pathologies and what to expect from the consultation. Book your appointment at one of our hospitals.

What is the speciality of infectious diseases?
The branch of medicine specialising in infectious diseases focuses on the study and prevention of pathologies caused by contagious agents such as viruses, bacteria, fungi, parasites or protozoa.
The treatment of these diseases requires the joint work of doctors with a thorough knowledge of their behaviour and specialists in the affected areas, especially in internal medicine.
What does the speciality of infectious diseases study?
The field of study of this speciality is very relevant to the health of all citizens and to other branches of medicine, as infectious diseases are one of the major causes of death today. Quirónsalud doctors divide their efforts into specific fields in order to further research:
- Microbiology: Includes the study of bacteria (bacteriology), viruses (virology), fungi (mycology) and parasites and protozoa (parasitology).
- Antibioticology: focuses mainly on raising awareness about the suitable use of antibiotics. On the one hand, it advises doctors on when to prescribe them and, on the other, it educates people on the importance of using them only when recommended by a doctor and according to their guidelines with a view to avoiding the development of resistance, and thus the loss of their effectiveness.
Which patients is it for?
At Quirónsalud, one of the most important tasks we carry out with regard to infectious diseases is to inform the entire population about prevention, focusing on the proper use of antibiotics and education in habits such as hand washing and the use of condoms during sex.
We also treat people suffering from infectious processes and provide immunity to those at higher risk of infection.
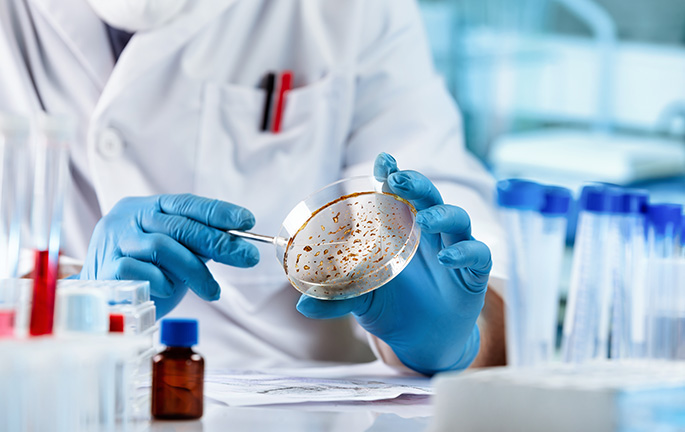
Techniques, procedures and diagnostic methods
The tests we perform to study the behaviour of infectious agents and to detect their possible presence in the human body are quite varied. The most widely used include:
- Blood test: a laboratory technique which uses serology tests to look for certain pathogens that may cause disease.
- Cultures: one of the most widely used methods to diagnose infectious diseases. It involves promoting the growth of micro-organisms present in the samples taken in the laboratory and testing for the presence of infectious agents.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): diagnoses infectious diseases after analysing a tissue, blood, saliva or mucus sample.
- Magnetic resonance: a diagnostic imaging method that allows specialists to see the condition of tissues affected by infection.
- Computerised axial tomography (CAT): uses three-dimensional X-ray images to obtain information, especially of soft tissues.
Diseases and symptoms
Main pathologies and diseases
Infectious disease physicians are trained and prepared to investigate, diagnose and treat a variety of infectious diseases, most notably, given their frequency, the following:
- Herpes zoster
- Mononucleosis
- Varicella
- Covid-19
- HIV
- AIDS
- Influenza or flu
- Hepatitis
- Salmonellosis
- Cholera
- Yellow fever
- Typhoid fever
- Tuberculosis
- Bacterial infections such as pneumococcus causing pneumonia, meningococcus causing meningitis, salmonella causing gastrointestinal infections, or staphylococcus producing skin and soft tissue infections, to name a few examples.
- Sexually transmitted infections by agents such as gonococcus, chlamydia, monkeypox virus, etc.
- Infections imported by travellers, driven by globalisation and climate change, such as yellow fever, malaria, dengue fever, among others transmitted by mosquito bites.
Related symptoms
The main symptom of infectious diseases is fever, although not always. Depending on the type of infection, the location, the causative micro-organism as well as the person suffering from the infection, the symptoms can be very varied, the most important of which include
- Diarrhoea
- Rash
- Cough
- Fatigue
- Muscular pain
- Swelling
- Problems with vision
- Lack of energy
- Weakness
- Breathing problems
About the infectious disease consultation
We solve any doubts you may have before you see the specialist
When the primary care doctor has difficulty identifying the source of an infection with clear symptoms, they refer the patient to the infectious disease consultation.
What should you keep in mind?
During your first appointment, the doctor will take your medical and family history and talk to you to find out the cause of the infection. This includes questions such as recent travel, possible contacts with people with an infectious disease, dietary habits, sexual relations or recent experiences with animals that can transmit diseases.
What should I take to the appointment?
Providing the specialist with as much information as possible is essential in order to reach an accurate diagnosis. To this end, we recommend that you come to the appointment with an exhaustive description of all the symptoms you have suffered, the diseases you may be suffering from and the treatments you are following.
You may receive a questionnaire a few days before your appointment asking about your medical history, usual medication and other specific questions that will allow us to anticipate certain aspects of your consultation, which will help us expedite and personalise your care. To do this, we recommend that you download the free Quirónsalud Patient Portal application, which will facilitate communication with your healthcare team.

If you have any further questions, please contact us through the Patient Services telephone number: 900 301 013