Breast Tomosynthesis
Tomosynthesis is a more advanced form of mammography that uses X-rays to obtain images of the breast from different angles.
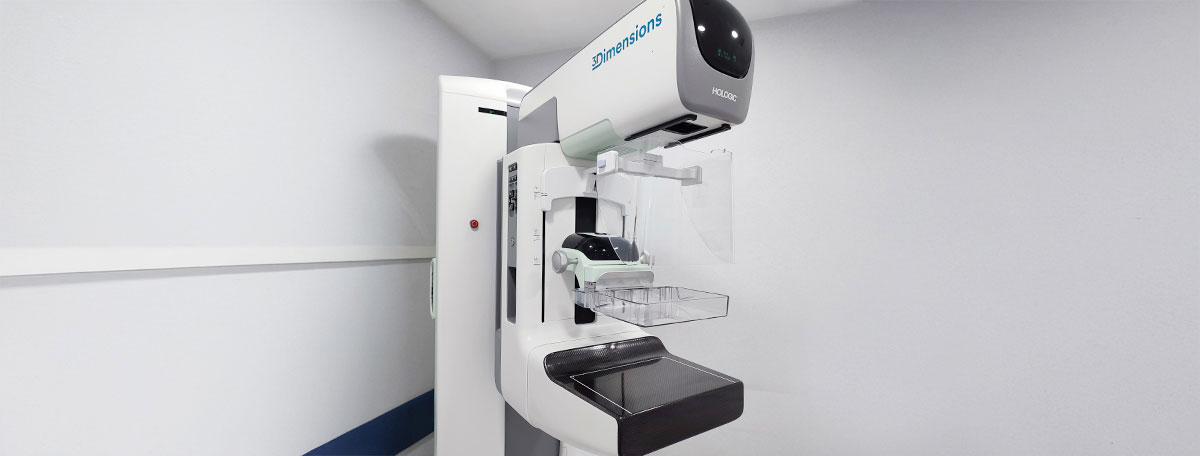
Tomosynthesis, also known as 3D mammography, is an imaging diagnostic test that uses X-rays to create three-dimensional images of the breast. This advanced technology emits energy beams from various angles to later overlap all the slices (about one millimeter each) and create a volumetric representation of the breast.
By providing detailed information and being able to obtain clear images even of dense breasts, it aids in the early diagnosis of breast cancer. It is also useful for detecting benign cysts or calcifications.
The precision of 3D mammography allows for the detection of small tumors that may go unnoticed in other types of diagnostic tests. For this reason, it is a suitable technology for breast cancer screenings.
How does it work?
Tomosynthesis uses X-rays, which are electromagnetic waves, to capture images. In this process, a device emits energy beams that pass through the breast tissue (depending on its density, the tissue absorbs the beams to varying extents). Once they exit the body, a radiation-sensitive plate records the electrical signals produced and translates them into images.
To obtain three-dimensional images, the device moves across the entire surface of the breast, capturing images as it passes. Since the images are digital, computer software combines them to create a three-dimensional representation.
The radiation used in the process is very low, so it does not negatively affect the patient's health. In any case, the benefits of the test far outweigh the risks.
What are the benefits of tomosynthesis?
The benefits of tomosynthesis are numerous. Some of the most prominent include:
- More precise and higher-quality images.
- Greater ease in distinguishing between cancerous and benign masses.
- Less breast compression compared to a mammogram, reducing discomfort.
- Shorter test duration.
- Ability to adjust the light and contrast of images.
- More accurate diagnosis.
When is it indicated?
Tomosynthesis is recommended for patients with suspicious results from other previously performed tests or those with a high risk factor.
By providing more precise images, it is especially indicated for women between the ages of 40 and 50, when breast tissue becomes denser. It is also suitable for younger women with dense breasts.
What to expect from tomosynthesis
Tomosynthesis is an outpatient procedure, meaning you can resume your normal routine once it is completed. It is recommended not to use deodorants, cologne, or talcum powder on your armpits and chest before your appointment, as these can interfere with image acquisition.
You will need to undress from the waist up. To preserve the patient's privacy, a fabric or paper gown is provided. Once in the examination room, your breast is placed on the platform beneath which the receptor plate is located, and it is gently compressed by the X-ray emitting device. This compression is not uncomfortable and is less than that required for a mammogram.
The head of the device moves across the breast to take the images, but the patient does not feel this movement. The process lasts around 15 minutes.
Specialties in which it is used
Radiology specialists are responsible for performing and interpreting the results of tomosynthesis at the request of gynecologists or oncologists.
















