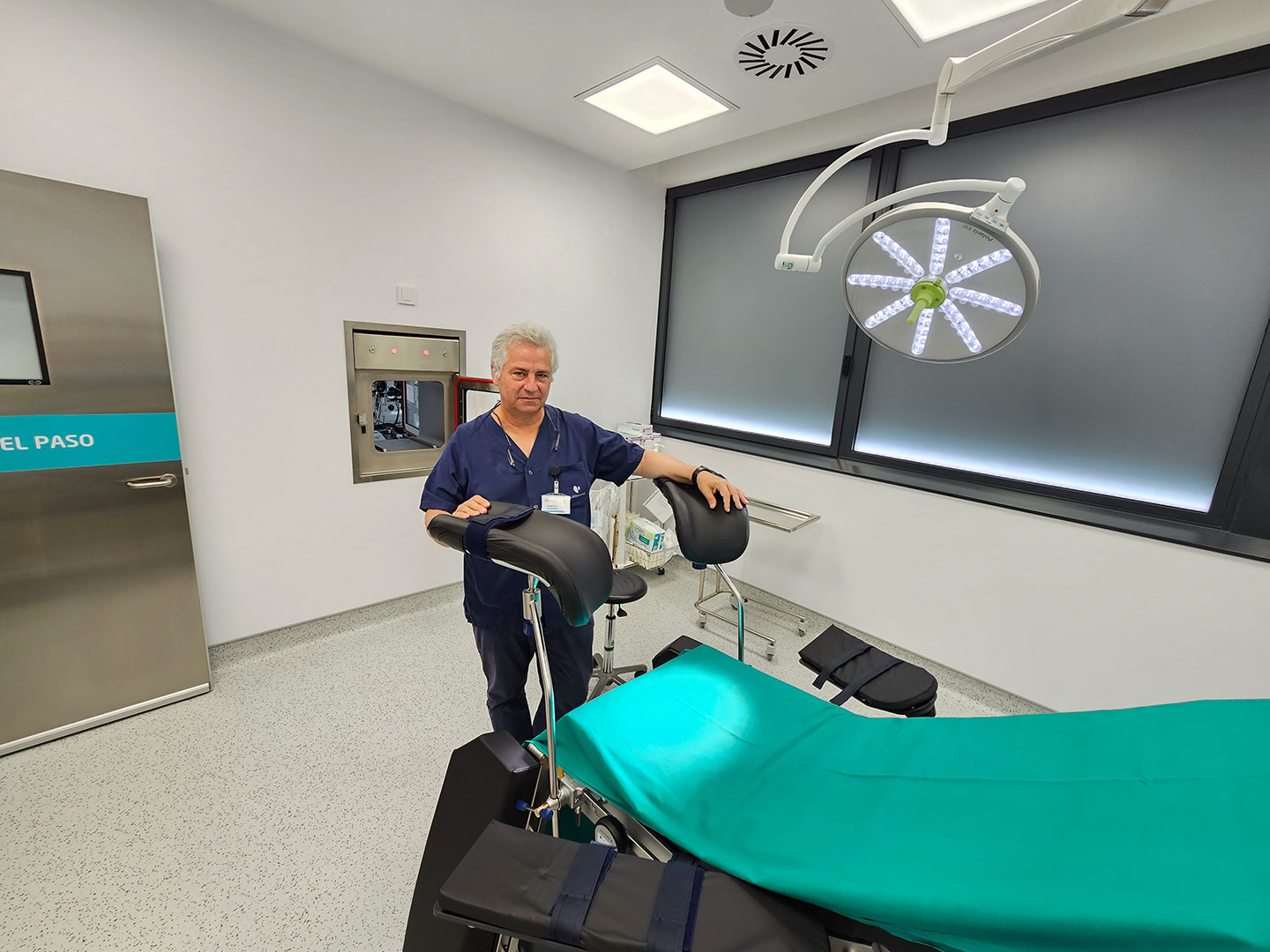
Assisted reproduction
Get informed about assisted reproduction and the various techniques involved. We explain the differences between artificial insemination and in vitro fertilization, and discuss the reasons why individuals visit a fertility clinic. Schedule your appointment at one of our hospitals.

What is Assisted Reproduction?
Assisted reproduction is a subspecialty of gynecology focused on the development and application of techniques designed to facilitate pregnancy in individuals experiencing difficulty conceiving naturally. It also provides options for fertility preservation in individuals planning to have children in the future.
What Does Assisted Reproduction Involve?
This medical specialty, focused on fertility, is dedicated to studying the causes of infertility and developing techniques to achieve pregnancy. The unit encompasses four distinct areas:
- Diagnosis: Genetic testing, clinical analysis, and physical examinations are performed to identify the underlying causes of infertility.
- Fertility Preservation: Enables the cryopreservation of oocytes, spermatozoa, or reproductive tissue for future use.
- Reproductive Treatments: Specific therapies are applied to address infertility and facilitate conception.
- Psychological Support: Mental health care is essential for women undergoing assisted reproduction procedures, helping maintain emotional well-being throughout treatment.
Who Is It For?
Assisted reproduction is intended for patients with infertility who are seeking to achieve pregnancy. It also caters to individuals who, due to personal circumstances, cannot conceive through conventional means, such as single women or female couples.
Techniques, Procedures, and Diagnostic Methods
Recent advancements in assisted reproduction have led to highly accurate diagnostic techniques and reproductive procedures with high success rates. Currently, there are three main methods:
- Artificial Insemination: Following ovarian stimulation, a processed semen sample is introduced into the uterus at the estimated time of ovulation. The semen, whether from a partner or donor, is prepared to select the most viable spermatozoa.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): After ovarian stimulation, oocytes are retrieved from the prospective mother or donor. Selected sperm are placed with the oocyte in the laboratory, allowing fertilization to occur. Embryos are transferred into the uterus via catheter on day 3 or 5, once cell division has begun.
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): A variant of IVF that offers improved outcomes. A single sperm is injected directly into the oocyte, which is then cultured in an incubator mimicking the human body’s conditions in terms of temperature, humidity, and gas concentration.
Diseases and symptoms
Main Pathologies and Conditions
Conditions commonly associated with infertility include:
- Male infertility
- Female infertility
- Endometriosis
- Hereditary diseases
- Recurrent miscarriages
- Pelvic infections
- Uterine fibroids (leiomyomas)
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Related Symptoms
While symptoms leading to assisted reproduction consultations are limited, they are typically unmistakable:
- Inability to achieve pregnancy
- Recurrent early pregnancy loss
Infertility causes are identified during the consultation process through diagnostic testing. Common causes include:
- Diminished ovarian reserve
- Poor oocyte quality
- Azoospermia (absence of sperm)
- Poor semen quality
- Genetic abnormalities
- Implantation disorders
- Fallopian tube obstruction
- Uterine malformations
- Ovulatory disorders
About the Assisted Reproduction Consultation
We solve any doubts you may have before you see the specialist
It is recommended to seek consultation after one year of unsuccessful attempts to conceive, or after six months if the woman is over 35.
During the initial visit, the specialist will take a thorough personal and family medical history and perform a physical examination. Additional tests are ordered to assess hormone levels, anatomical anomalies, or any medical conditions that may affect fertility.
What Should You Consider?
It is important to be mentally prepared for the waiting periods associated with testing and treatment. Reproductive treatments follow specific timelines that cannot be expedited. Psychological support is advisable to help manage the emotional stress that may arise during the treatment process.
What Should I Bring to the Appointment?
Previous test results and medical reports are highly beneficial for the reproductive medicine specialist. It is recommended to bring a detailed family history—especially on the maternal side—and a summary of all prior steps taken before the consultation.

If you have any further questions, please contact us through the Patient Services telephone number: 900 301 013