Helium-Free Magnetic Resonance
Helium-free magnetic resonance is an imaging diagnostic test that minimizes the use of helium required to keep the magnets in the proper state for operation. It is an innovative and sustainable technology that does not compromise the quality of the diagnosis.
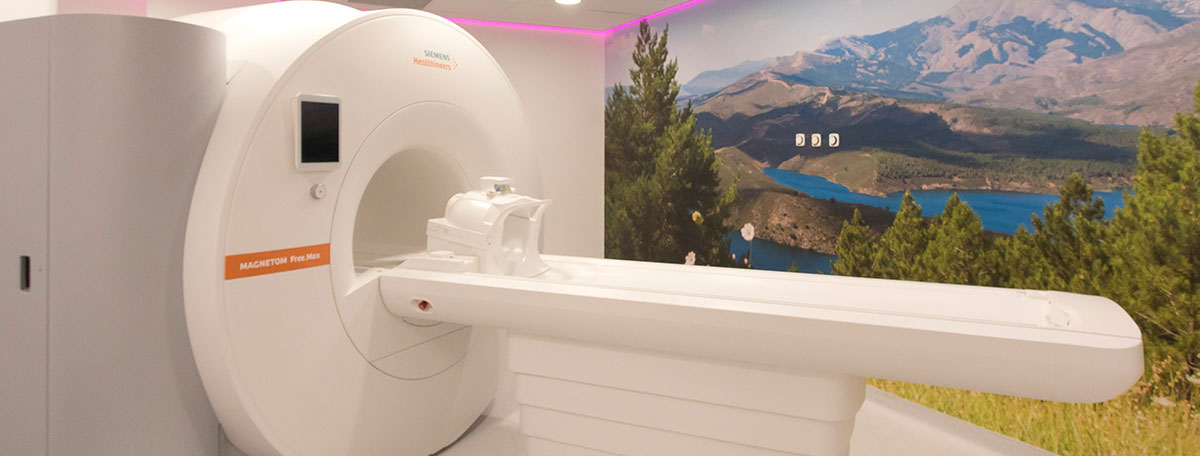
Helium is a noble gas that remains in a liquid state even at very low temperatures (its boiling point is -269°C). For this reason, it is used in traditional magnetic resonance devices to cool the coils that generate the magnetic fields and ensure they are stable and uniform.
Helium-free magnetic resonance devices operate with innovative technology that reduces the use of this scarce natural resource to a minimum. The coils are coated with the necessary helium to keep them at a low temperature (about 7 liters, compared to the 1,500 liters that might be used to recharge conventional devices), and then they are sealed to prevent further refilling.
Helium-free MRIs maintain the same magnetic power, ensuring excellent quality images for accurate diagnoses with a more sustainable and lighter device.
How does it work?
The operation of helium-free magnetic resonance is the same as the traditional method:
- The patient is placed inside the MRI device, in the form of a tube.
- The coils generate an electromagnetic field that acts like a magnet and emits radiofrequency waves.
- The hydrogen atoms in the water molecules of the body absorb energy in the presence of the electromagnetic field as they fight to maintain their position and avoid being attracted to the magnet.
- This energy, which manifests in waves, is captured by the receiver coils.
- The software transforms the signals into images.
The difference lies in how the device maintains the correct temperature:
- Conventional MRI: Liquid helium is stored in a reservoir. When needed, it circulates through pipes around the coils to absorb the heat they generate when in use, turning into gas, and then returns to the reservoir to be cooled again. Some helium is lost in the process, so it needs to be recharged periodically to ensure the device works properly.
- Helium-free MRI: Liquid helium is introduced into a chamber surrounding the coils and sealed so it cannot escape, regardless of its state. Therefore, refilling is unnecessary.
What are the benefits of helium-free magnetic resonance?
Using helium-free MRI devices offers many benefits:
- Minimal helium consumption.
- Sealed system that prevents leaks.
- Lighter device.
- Reduced safety requirements, as no pipes are needed to conduct the helium.
- No pipes mean more flexible placement options, and it can even be mobile.
- Excellent image quality.
- Lower economic costs.
- Reduced environmental impact.
When is it indicated?
Helium-free magnetic resonance is used for the same purposes as the conventional procedure:
- Neurology: Brain damage, dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, aneurysms, strokes, tumors.
- Cardiology: Obstructions, inflammations, structural alterations within the heart.
- Traumatology: Injuries or tumors in bones, ligaments, or cartilage.
- Gynecology: Breast cancer, uterine abnormalities.
- General Surgery and Digestive System: Tumors or malformations in the liver, kidneys, or pancreas.
What to expect from helium-free magnetic resonance
The test with helium-free magnetic resonance is outpatient, meaning the patient does not need to be hospitalized and can return to their routine once completed.
Since an electromagnetic field is generated, all metallic items, makeup, nail polish, and clothing must be removed to enter the radiology room. The medical center provides a gown and special foot covers.
Occasionally, a contrast substance is administered intravenously, with a line inserted into a vein in the arm. The patient lies on the stretcher, positioning themselves based on the area to be studied, and receiver coils are placed. It is important to remain as still as possible to avoid distorted images.
During image capture, healthcare staff leave the room and monitor the patient through cameras and a glass wall. They also have microphones for communication and can alert the patient in case of an emergency.
The duration of a helium-free MRI varies between 30 and 60 minutes, depending on the specific case.
Specialties in which it is used
Helium-free magnetic resonance is used in the radiology specialty, as requested by neurology, cardiology, gynecology, general surgery and digestive system, traumatology, rheumatology, nephrology, oncology, or urology.














