SPECT-TAC
The SPECT-TAC is a diagnostic test that combines three-dimensional anatomical images with metabolic and functional information from the internal organs of the body.
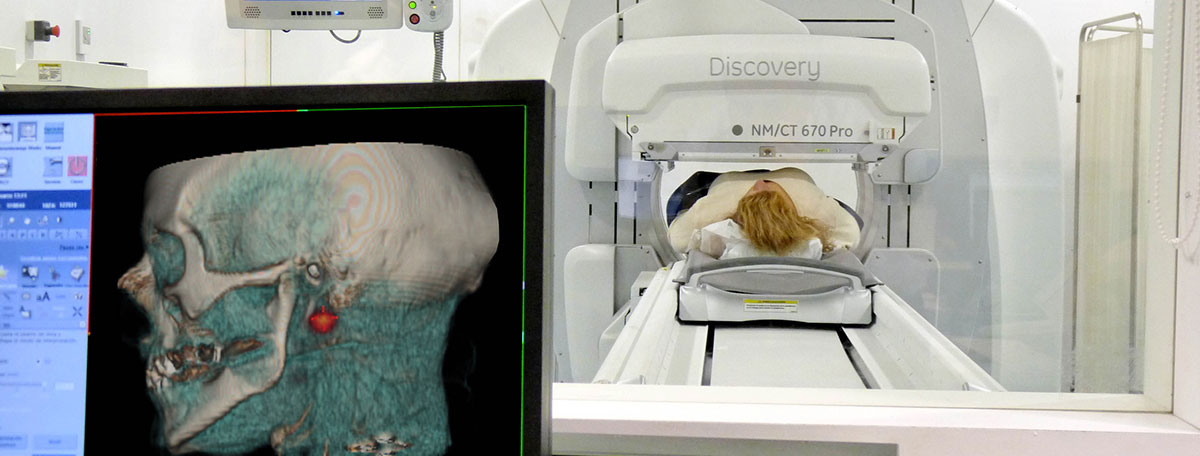
The SPECT-TAC is a diagnostic test that combines Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) and Computed Tomography (CT). As a result, functional and structural three-dimensional images are obtained, along with an anatomical image of the structures. Ultimately, better information about the patient’s condition is gathered, facilitating both the diagnosis and the exact localization of lesions.
The Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) uses gamma rays in doses that are safe for the body. The SPECT-TAC scan is shorter, which significantly reduces the exposure time, increasing patient safety.
SPECT-TAC technology is highly useful in oncology, especially for locating the sentinel node in breast cancer, as well as for evaluating spinal and coronary pathologies.
How does it work?
The SPECT-TAC process consists of the combination of both tests without the need to move the patient:
- A radiopharmaceutical is administered intravenously (technetium-99m is the most commonly used).
- The patient is placed in the gamma camera, which emits photons and records the movement of energy within the body.
- X-rays are emitted from various angles to obtain cross-sectional images, which are then combined to reconstruct a 3D model of the body’s structures.
- The function and anatomy of the organ under study are evaluated in a single image.
What are the benefits of SPECT-TAC?
SPECT-TAC studies have important benefits:
- Better diagnosis.
- Reduced duration of the test (estimated to be halved).
- Less radiation exposure to the patient (around 50% less than conventional tests).
When is it indicated?
SPECT-TAC is highly useful for diagnosing diseases in various specialties:
- Oncology: Breast, thyroid, neural crest, or adrenal gland tumors.
- Cardiology: Coronary or ischemic heart disease.
- Traumatology: Spinal disorders, bone infections, joint inflammation, or metastases.
- Radiocirugía: Detection of the sentinel node (the first lymph node to which cancer spreads from an adjacent organ).
What to expect from SPECT-TAC
The SPECT-TAC procedure is outpatient, meaning no hospital admission is required.
Before entering the room where the test will take place, the patient must remove any metal items they are wearing (jewelry, glasses, hearing aids, dentures, some types of makeup), as well as their clothing, since a gown will be provided by the medical center.
After signing the informed consent, the patient lies on the examination table. The radiopharmaceutical is administered through an intravenous line placed in one of the veins in the arm or hand. The injection is the only slightly painful part of the process. It typically takes about an hour for the radiotracer to circulate through the body. After that, the examination table is moved into the gamma camera, which is tube-shaped and rotates around the patient. Image capture usually takes about 30 minutes.
Specialties in which it is used
Nuclear medicine specialists are responsible for performing the SPECT-TAC and preparing the report of results. This test is highly useful in oncology, traumatology, cardiology, and radiocirugía.























