Hospital Radiation Physics
Learn about the field of hospital radiation physics and its scope of study. We explain how radiation protection is carried out in nuclear medicine to ensure patient safety, as well as the key procedures in medical physics.

What is Hospital Radiation Physics?
Hospital radiation physics is a specialty that assists in the planning and application of various radiological techniques by measuring and assessing radiation. Its primary goal is to ensure the safety of the patient during treatment or diagnostic tests.
Hospital radiation physics technicians work alongside specialized physicians in nuclear medicine and radiology.
What Does Hospital Radiation Physics Study and Treat?
The study of medical physics is extensive, as its scope in the hospital is broad and requires a wide range of specific knowledge. Specialists in hospital radiation physics research radiation, establish safety protocols, and even administer treatments. Some of their most important tasks include:
- Radiation Protection: Hospital physicists use their knowledge to design facilities and determine where shielding should be placed. They also manage personal protective equipment (PPE) for both patients and medical staff and ensure legal requirements in this area are met, serving as the main liaison with regulatory bodies.
- Dosimetry in Radiotherapy: They ensure radiation doses remain within established limits. They also review the history of medical staff, nurses, and technicians to avoid excessive exposure.
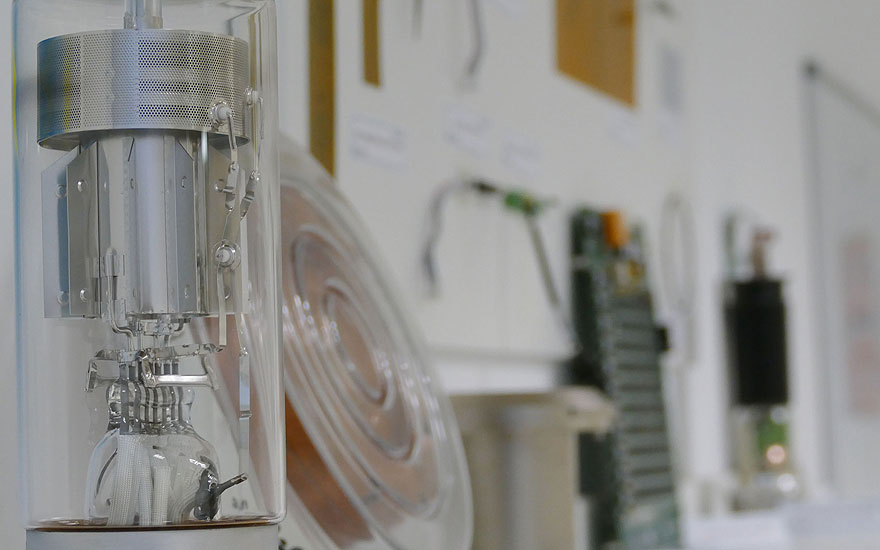
- Quality Control: This ensures that equipment functions properly and that emitted radiation meets the prescribed standards. In this area, hospital physicists also calibrate emission detectors and establish protocols for action.
Techniques, Procedures, and Diagnostic Methods
Techniques used in hospitals related to medical physics can be diagnostic or therapeutic. In either case, specialists in radiological safety must oversee how these procedures are carried out. Some of the most commonly used procedures include:
- X-rays: A diagnostic imaging method that uses electromagnetic waves (a form of radiation) to view the body's internal organs. Hospital physicists monitor the appropriate settings, ensure the correct dose for the patient, and verify that the equipment is in good condition.
- Linear Electron Accelerator Treatment: A procedure where a medical linear accelerator (LINAC) is used to apply X-rays precisely to the shape of a tumor. Radiological safety must be monitored by measuring the applied dose and treatment duration.
- Stereotactic Brain Radiosurgery (SRS): A surgical technique that uses a gamma ray knife for neurosurgical operations. The hospital physicist administers the required dose and prepares a treatment plan that takes the patient's characteristics into account.
- Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT): A treatment that uses high-precision radiation to treat localized lesions outside the skull. Due to high doses, fewer sessions are required, but stringent safety measures and dose monitoring are essential.
- Brachytherapy: A procedure where internal radiotherapy is applied. Radioactive seeds or capsules are placed as close to the tumor as possible, or even inside it. There are different types of brachytherapy depending on where the radiopharmaceutical is placed: interstitial (inside the tumor) or intracavitary (in a cavity near cancerous cells). Hospital physicists determine the dose and the most effective location for administration.
In all cases, operating rooms or diagnostic areas must be protected to prevent radiation from spreading to other parts of the hospital. Access to these areas is restricted to authorized individuals, typically patients and essential medical staff. Personnel involved in these procedures must always wear PPE and carry their personal dosimeter.