Radiodiagnosis
Discover everything related to radiodiagnosis. We explain what it is, its field of study, what it is used for, the techniques and procedures it uses, and the importance of this medical specialty. Book your appointment at one of our hospitals.

What is radiodiagnosis?
The medical specialty of radiodiagnosis is responsible for detecting diseases and injuries. Specialists in this field of medicine analyze images obtained through various techniques to determine whether a pathology exists and how it can be treated.
Radiologists work together with other healthcare professionals to provide an accurate diagnosis, establish the most appropriate treatments, determine the surgical processes that best suit each patient’s characteristics, and assess the effectiveness of the medication administered.
What does radiodiagnosis study and treat?
Radiology focuses on the different technologies used to obtain images of the inside of the human body to diagnose or rule out certain pathologies. Since these procedures can be applied to different areas of the body, radiologists may specialize in more specific areas to provide even more personalized care to patients:
- Neuroradiology: aimed at detecting alterations in the brain and nervous system.
- Vascular radiology: considered an interventional radiology specialty because the procedures carried out to observe the state of the venous, arterial, and lymphatic systems often also serve to treat most of the pathologies that manifest.
- Pediatric radiology: specializes in the specific characteristics of children and adolescents.
- Abdominal radiology: focused on observing the condition of abdominal organs such as the spleen, intestines, stomach, kidneys, bladder, or urethra.
- Breast radiology: focused exclusively on breast health, and most of the time, preventive tests are performed.
Techniques, procedures, and diagnostic methods
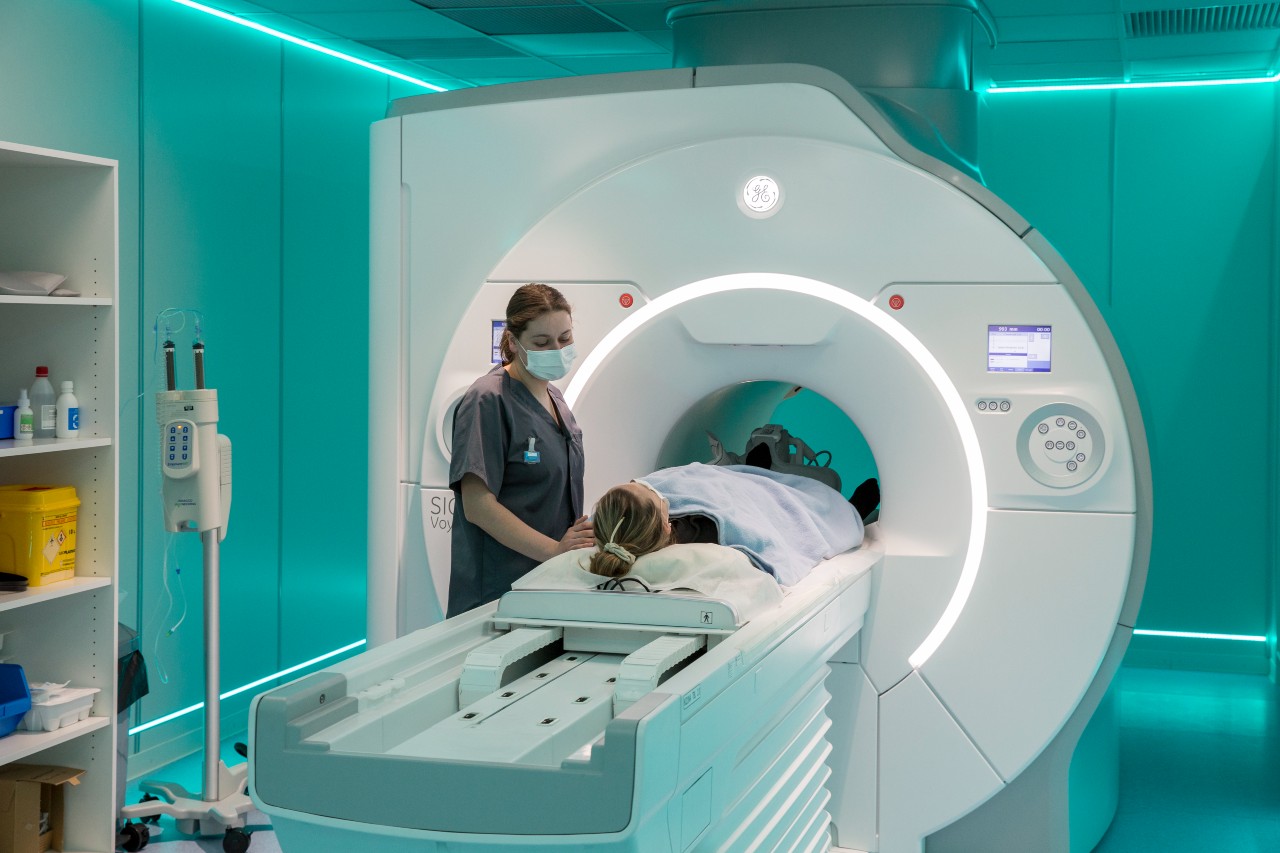
There are many imaging techniques used in radiodiagnosis, and over the years, they have become increasingly advanced and precise. Thanks to this development and the high specialization of radiologists, it is possible to determine an accurate diagnosis and understand the characteristics of the disease in order to establish an appropriate treatment plan. Some of the most common procedures include:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): provides images of the body in two or three dimensions using radiofrequency waves. It is commonly used to detect degenerative diseases, tumors, or infectious processes.
- Computed Tomography (CT scan): uses X-rays to obtain images of internal organs. This technique allows viewing sections of bones, organs, and tissues that can be studied separately in two dimensions or together, creating a three-dimensional view.
- Ultrasound: a procedure that creates two-dimensional images using ultrasound waves, providing faster results compared to other techniques.
- Mammography: an X-ray used to examine the condition of the mammary gland.