Paediatrics
Find out everything you need to know about paediatrics and its broad field of study. We tell you what its main function is, what routine check-ups involve, which childhood diseases are most commonly treated and how to help children feel safe when they go to the doctor. Book an appointment with a paediatrician at one of our hospitals.
What is paediatrics?
Paediatrics is the speciality that treats children from birth to adolescence. Its area of expertise is oriented towards the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of specific diseases and medical conditions affecting children during their development.
Paediatricians are highly trained medical professionals with specific knowledge about the normal growth and development of children, as well as the most common and complex paediatric conditions. Their work extends beyond medical treatment to include guidance to parents and caregivers on issues related to parenting, nutrition, immunisation and the emotional development of children.
What does paediatrics study?
Our paediatrics units study the natural development of children and deal with the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of childhood diseases. There are several subspecialties within paediatrics that allow physicians to specialise in specific medical areas related to the paediatric population. Some of these specialities include:
- General paediatrics: focuses on well-child check-ups, health education and monitoring of the vaccination schedule. It also treats minor pathologies that do not require specialisation.
- Neonatology: focuses on the medical care of newborns born prematurely or with severe medical problems in the first 4 weeks of life. Neonatologists work in multidisciplinary teams in neonatal intensive care units (NICU) where they work closely with other healthcare professionals, such as specialised nurses, paediatric surgeons and other specialists, to provide high-quality, holistic care for newborns and their families.
This area is also responsible for Perinatal Counselling, where, as part of a multidisciplinary team together with obstetricians and other specialists, doctors make a perinatal Diagnosis of diseases in the unborn foetus using techniques such as foetal magnetic resonance imaging and high-resolution ultrasound.
- Paediatric intensive care: this branch of medicine focuses on the advanced and specialised care of children and adolescents with serious diseases or those in critical condition.
- Developmental and Behavioural Paediatrics: Focuses on the diagnosis and management of developmental and behavioural disorders, such as autism and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
It is important to note that every medical speciality that treats adults, has its equivalent for children. For example, there are branches such as neuropaediatrics, which deals with child neurological disorders; paediatric dermatology, which focuses on childhood skin conditions; paediatric nephrology, which deals with kidney problems in children; as well as paediatric psychology, which deals with children’s mental health. In addition, other specialties such as rheumatology, cardiology, ophthalmology and endocrinology also have their specific paediatric healthcare equivalents.
Which patients is it for?
Paediatrics is a comprehensive, multidisciplinary specialty that focuses on the medical care and holistic development of children and adolescents. In addition to addressing the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of diseases specific to this stage of life, paediatrics also benefits from collaboration with various other medical disciplines and healthcare professionals to ensure comprehensive and holistic care for young patients.
Techniques, procedures and diagnostic methods
In paediatrics, we use diagnostic methods to assess the health and wellbeing of children and adolescents. These tools are essential to identify medical conditions, monitor development and ensure an accurate approach to paediatric healthcare. Some of the most common diagnostic methods include:
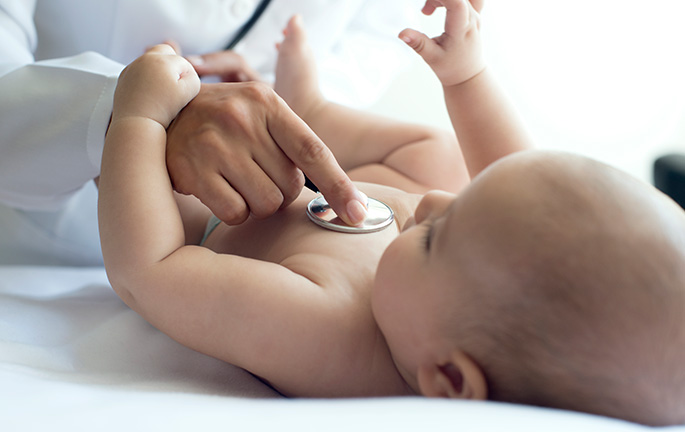
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Getting a detailed medical history and performing a thorough physical examination are the starting point in any paediatric diagnosis. Paediatricians ask about symptoms, family and personal history, and lifestyle habits to get a full picture of the patient’s situation.
- Laboratory tests Blood and urine tests, as well as other biological fluid analyses provide valuable information on organ function, nutrient levels, inflammatory markers and more. These tests may include complete blood counts, biochemical profiles, and liver and kidney function tests.
- Imaging tests: Techniques such as radiography, ultrasound, computerised tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allow visualisation of internal body structures to detect abnormalities, injuries or developmental problems.
- Echocardiography: Echocardiography: A type of ultrasound that focuses on the heart, allowing evaluation of cardiac function and anatomy for congenital defects or other conditions.
Procedures ranging from vaccinations to common ER procedures such as stitches, oxygen therapy and bladder catheterisation are also performed in paediatrics.
Diseases and symptoms
Main pathologies and diseases
The childhood diseases most frequently found in a paediatric primary care consultation are:
- Sinusitis
- Gastroenteritis
- Conjunctivitis
- Bronchitis
- Bronchiolitis
- Meningitis
- Cystitis
- Varicella
- Streptococcal tonsillopharyngitis
- Flu
- Rubella
- Asthma
Related symptoms
Some of the most common symptoms for which children come for a consultation are:
About the paediatrics consultation
We solve any doubts you may have before you see the specialist
There are two different types of paediatrics consultations. On the one hand, there are routine appointments for age-appropriate check-ups and child vaccination. On the other, children have to go to the doctor due to illnesses which, depending on their nature, will be treated by the general paediatrician or referred to a specialist, as is the case with adults.
What should you keep in mind?
Before going to the paediatrician we advise preparing the child so that they know what is going to happen. This will help them stay calm and be more trusting of the doctor. Preparing a child for the paediatrician involves using simple, positive language and answering questions. Reading books about doctors and playing doctor at home can help. Avoid threats and focus on sensations, such as explaining that the doctor will check their body. Let the child bring a toy for comfort, keep calm and get there early so the child can explore the waiting room.
We also recommend dressing your child in comfortable, easy-to-remove clothes to shorten the visit, as well as bringing spare nappies, food and toys to entertain your child. This will allow you to ask all the questions you need without interruption.
What should I take to the appointment?
In the case of routine check-ups, you should bring your child’s record book so that the paediatrician can keep track of your child’s growth and note down any vaccinations received. These appointments are also the perfect time to ask any questions about the upbringing and care of your baby, especially in the first months of life. We advise you to write down all the points you want to discuss in order not to forget anything.
In consultations relating to illness, it is a good idea to have the symptoms written down and to bring any tests that have been carried out previously.
You may receive a questionnaire a few days before your appointment asking about your medical history, usual medication and other specific questions that will allow us to anticipate certain aspects of your consultation, helping us to expedite and personalise your care. To do this, we recommend that you download the free Quirónsalud Patient Portal application, which will facilitate communication with your healthcare team.

If you have any further questions, please contact us through the Patient Services telephone number: 900 301 013